Structure and Function of Trunnion Mounted Ball Valve Seats
On this page
Trunnion-mounted ball valves are common fluid control devices that primarily regulate fluid flow through the rotation of a spherical element supported by trunnions. The valve seat, as a core component of the trunnion-mounted ball valve, plays a crucial role in influencing the valve's performance, longevity, and adaptability. This article will delve into the structural features, operational principles, performance advantages, and significance of trunnion-mounted ball valve seats in practical applications, as well as current trends in their development.
The design of the trunnion-mounted ball valve seat not only serves the fundamental sealing function but also plays a vital role in regulating fluid flow. There are primarily two types of valve seats: automatic release valve seats and double-seal valve seats. Each type has distinct characteristics, allowing them to meet different operational demands.
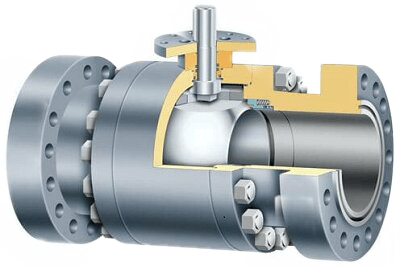
Automatic release valve seats are specially designed to address varying pressure conditions and ensure the safety and stability of the system. Their unique bi-directional cutoff capability allows them to automatically adjust according to the direction of fluid flow, thereby achieving effective control of the medium. Below, we will explore their structural principles, key components, and their importance in practical applications.
Automatic release valve seats are designed for self-adjustment in response to pressure variations. These seats possess the ability to cut off fluid in both directions, effectively preventing backflow and ensuring the safety and stability of the system.
Inlet End Seat: When the pressure at the inlet end exceeds the pressure in the valve chamber, the pressure differential forces the seat to seal, cutting off the flow of fluid from the inlet and preventing backflow, thus protecting the system's normal operation.
Outlet End Seat: When the pressure in the valve chamber exceeds the pressure at the outlet end, a pressure differential similarly drives the outlet seat to open, facilitating the automatic release of chamber pressure. This design ensures that the system can respond quickly under abnormal conditions, reducing potential risks.
The primary components of an automatic release valve seat include:
Seat: Made from corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant materials to maintain good sealing performance in high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
Seal Ring: Constructed from high-performance materials such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) to enhance the sealing effect and effectively prevent fluid leakage.
Spring: A helical or disc spring provides dynamic support and sealing force, ensuring the seat's reliability under varying working conditions.
O-ring: Used to ensure a good seal between the seat and the valve body, preventing medium leakage.
Double-seal valve seats enhance sealing performance by adjusting the position of the seal ring and the O-ring or by altering the dimensions of the seat tail, a design referred to as the "dual piston effect." This design improves the sealing effectiveness and reliability of the seat, making it suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Below, we will briefly discuss its structural principles and application areas.
Double-seal valve seats achieve efficient dual sealing functionality through precise adjustments of the relative positions of the seal ring and O-ring or by modifying the dimensions of the seat tail. This design, known as the "dual piston effect," not only enhances sealing performance but also improves the adaptability of the seat.
Inlet End Seat: When the pressure at the inlet end exceeds the pressure in the valve chamber, the pressure differential forces the seat to seal, cutting off the flow of fluid and ensuring smooth flow.
Outlet End Seat: When the pressure within the chamber exceeds that at the outlet end, the pressure acting on the outlet seat also creates a pressure differential that seals the seat, preventing fluid from flowing from the chamber to the outlet, thereby achieving dual sealing effects.
Double-seal valve seats offer a wide array of significant advantages, making them highly valuable in a variety of industrial applications.
Isolation Design: Both seats provide fluid cutoff capability in both directions, allowing them to adapt to complex fluid control requirements, particularly in scenarios requiring tight control over fluid flow.
High Sealing Performance: The dual-seal design effectively prevents fluid leakage, ensuring the safety and hygiene of the system, thereby meeting the stringent quality requirements in various applications.
Strong Pressure Resistance: In high-pressure applications, double-seal valve seats maintain stable performance, effectively preventing valve failure and ensuring the long-term reliability of equipment.
The design and function of trunnion-mounted ball valve seats are crucial in fluid control systems. The flexible application of automatic release and double-seal valve seats not only enhances the sealing performance and safety of the valves but also meets the fluid control needs of various industries. As technology continues to advance and application areas expand, trunnion-mounted ball valve seats will play an increasingly important role, providing robust support for safe and efficient fluid control.
