A Complete Manual on Plug Valve: Structure, Functionality and Maintenance
In the realm of pressure pipelines, a remarkable solution has emerged - the Plug Valves. This quarter-turn valve boasts a unique structure and working principle, making it a versatile and reliable choice for directing fluid flow. This article explores the essence of Plug Valve, its efficient working principle, and offers insights into fault diagnosis, maintenance, and care, ensuring optimal performance in various applications.
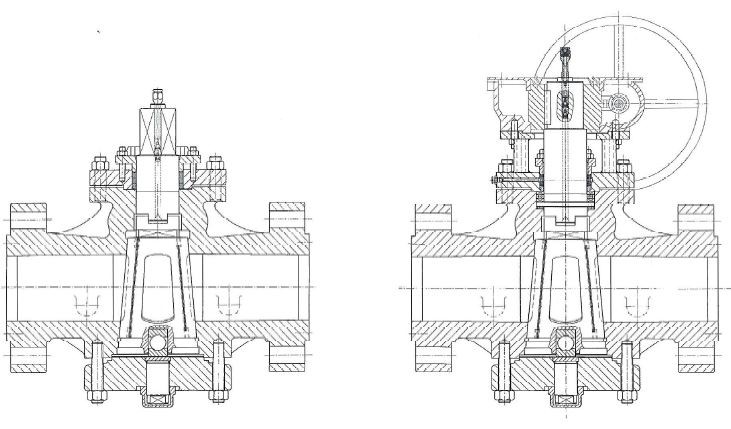
1. Introduction: Unlocking the Potential of Plug Valve Technology
The Plug Valve, a quarter-turn marvel, facilitates fluid flow control through its cylindrical or conical plug. Unlike traditional valves, the linear opening of the plug ensures a consistent flow area, making it ideal for a wide range of applications, especially under throttling conditions. Its adaptability to various flow areas and shapes sets it apart in the world of fluid control technology.
2. Equipment Structure and Applications: A Closer Look
The core components of a Plug Valve include the valve body, plug, and packing. This simple yet effective structure finds primary applications in line purging, bypassing, and venting within pipeline systems. The valve's design lends itself to seamless integration into diverse operational scenarios.
3. Working Principle: Precision in Throttling Conditions
In throttling conditions, the plug assumes a central position, inducing two pressure drops in the fluid. As the plug rotates from the fully open position, the inlet's flow area decreases, causing an initial pressure drop. Subsequently, the fluid enters the inner side of the plug within the fully open area, undergoes pressure restoration, and experiences another throttling at the outlet. The diverse designs of the plug, especially in conical seat configurations, showcase its versatility in handling throttling conditions. The plug's engagement with the seat, when sealed with grease, ensures efficient fluid control.
4. Operation: Simple and Strict
Valve operation remains a manual, single-person task, with strict adherence to prohibiting force amplifiers or multiple operators. The steps include careful inspection of open/close indicators, followed by a precise rotation of the handwheel for full opening or closing. Excessive force is discouraged, and short-term throttling is permissible, but long-term throttling is strictly prohibited.
5. Inspection, Maintenance, and Care: Ensuring Longevity
Regular inspections and maintenance are vital for sustained performance. Monthly checks assess valve flexibility, sealing points, and leakage prevention, while quarterly maintenance addresses corrosion, actuator functionality, and lubrication. A meticulous cleaning and repainting process ensures the equipment's durability.
6. Fault Diagnosis and Handling: A Proactive Approach
To tackle common issues, such as difficult switching operations or minor leakages, users are guided to employ straightforward measures. These include adding sealing grease, tightening loose screws, or adjusting packing for even distribution, guaranteeing the seamless operation of plug valves.
In conclusion, the Plug Valve stands as a beacon of efficiency in fluid control technology. By understanding its structure, working principles, and implementing regular maintenance, users can harness its full potential, ensuring a reliable and efficient fluid flow across diverse applications.

1. Introduction: Unlocking the Potential of Plug Valve Technology
The Plug Valve, a quarter-turn marvel, facilitates fluid flow control through its cylindrical or conical plug. Unlike traditional valves, the linear opening of the plug ensures a consistent flow area, making it ideal for a wide range of applications, especially under throttling conditions. Its adaptability to various flow areas and shapes sets it apart in the world of fluid control technology.
2. Equipment Structure and Applications: A Closer Look
The core components of a Plug Valve include the valve body, plug, and packing. This simple yet effective structure finds primary applications in line purging, bypassing, and venting within pipeline systems. The valve's design lends itself to seamless integration into diverse operational scenarios.
3. Working Principle: Precision in Throttling Conditions
In throttling conditions, the plug assumes a central position, inducing two pressure drops in the fluid. As the plug rotates from the fully open position, the inlet's flow area decreases, causing an initial pressure drop. Subsequently, the fluid enters the inner side of the plug within the fully open area, undergoes pressure restoration, and experiences another throttling at the outlet. The diverse designs of the plug, especially in conical seat configurations, showcase its versatility in handling throttling conditions. The plug's engagement with the seat, when sealed with grease, ensures efficient fluid control.
4. Operation: Simple and Strict
Valve operation remains a manual, single-person task, with strict adherence to prohibiting force amplifiers or multiple operators. The steps include careful inspection of open/close indicators, followed by a precise rotation of the handwheel for full opening or closing. Excessive force is discouraged, and short-term throttling is permissible, but long-term throttling is strictly prohibited.
5. Inspection, Maintenance, and Care: Ensuring Longevity
Regular inspections and maintenance are vital for sustained performance. Monthly checks assess valve flexibility, sealing points, and leakage prevention, while quarterly maintenance addresses corrosion, actuator functionality, and lubrication. A meticulous cleaning and repainting process ensures the equipment's durability.
6. Fault Diagnosis and Handling: A Proactive Approach
To tackle common issues, such as difficult switching operations or minor leakages, users are guided to employ straightforward measures. These include adding sealing grease, tightening loose screws, or adjusting packing for even distribution, guaranteeing the seamless operation of plug valves.
In conclusion, the Plug Valve stands as a beacon of efficiency in fluid control technology. By understanding its structure, working principles, and implementing regular maintenance, users can harness its full potential, ensuring a reliable and efficient fluid flow across diverse applications.

