Guidelines for Installing Swing Check Valves
In pipeline systems, selecting the appropriate check valve is paramount. The swing check valve, with its unique design, offers distinct advantages and versatile applications. This article presents an overview of the structural features, installation methods, and pertinent considerations for swing check valves, aiming to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding and practical insights into this essential check valve.
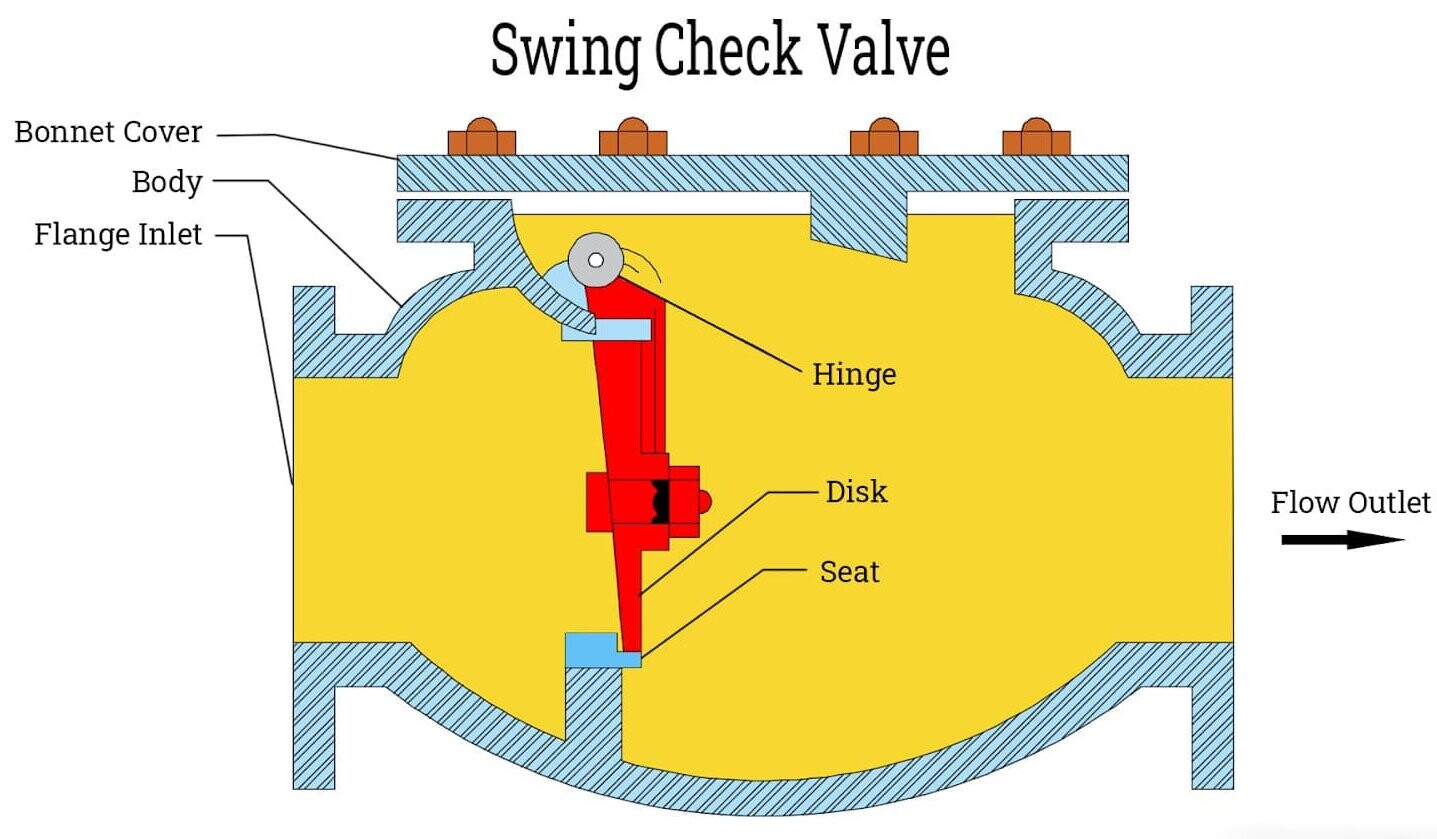
Structural Features and Application Scope
The swing check valve comprises a valve body, cover, disc, and lever. Its disc, shaped like a circular plate, rotates around the pin axis outside the valve seat passage. Unlike lift check valves, the internal passage of swing check valves adopts a streamlined design, resulting in lower flow resistance, particularly suitable for large-diameter pipelines. This valve type finds application across a spectrum of media including water, steam, oil products, nitric acid, acetic acid, strong oxidizing agents, and urea, making it indispensable in industries such as petroleum, chemical, pharmaceuticals, fertilizers, and power generation.
Installation Procedure
Key Considerations
Vertical Installation of Swing Check Valves
While swing check valves are typically installed on horizontal pipelines, they are also suitable for vertical installations when necessary. In such configurations, the medium flows from the bottom to the top of the vertical pipe. However, the choice between horizontal and vertical installation should be made based on comprehensive considerations of pipeline layout and system requirements.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the structural features, installation procedures, and considerations associated with swing check valves is essential for ensuring the efficient operation and longevity of pipeline systems. By adhering to proper installation practices and maintenance protocols, users can enhance system reliability and safety.

Structural Features and Application Scope
The swing check valve comprises a valve body, cover, disc, and lever. Its disc, shaped like a circular plate, rotates around the pin axis outside the valve seat passage. Unlike lift check valves, the internal passage of swing check valves adopts a streamlined design, resulting in lower flow resistance, particularly suitable for large-diameter pipelines. This valve type finds application across a spectrum of media including water, steam, oil products, nitric acid, acetic acid, strong oxidizing agents, and urea, making it indispensable in industries such as petroleum, chemical, pharmaceuticals, fertilizers, and power generation.
Installation Procedure
1. Preparation: Prior to installation, the swing check valve requires preparatory steps. This involves removing the plugs and foam boards at both ends of the valve passage, cleaning the inner cavity to eliminate oil residues, stripping off the oil paper from the disc surface, and removing any oil deposits.
2. Positioning: Select an appropriate installation location and mount the swing check valve onto the pipeline, ensuring the directional symbol on the valve corresponds to the flow direction to avoid misalignment.
3. Testing: Allow the medium to flow through the pipeline and verify whether the valve effectively prevents backflow, confirming its proper functioning.
2. Positioning: Select an appropriate installation location and mount the swing check valve onto the pipeline, ensuring the directional symbol on the valve corresponds to the flow direction to avoid misalignment.
3. Testing: Allow the medium to flow through the pipeline and verify whether the valve effectively prevents backflow, confirming its proper functioning.
Key Considerations
- Load Bearing: It's crucial to note that check valves within the pipeline cannot bear weight, especially for larger valves which should be independently installed to avoid being influenced by system pressure.
- Directional Markings: The directional markings on the valve body should align with the direction of fluid flow to ensure optimal valve operation.
- Medium Characteristics: The medium passing through the pipeline should not contain hard particles to prevent damage to the sealing surfaces. Therefore, swing check valves are unsuitable for media with solid particles or high viscosity.
- Installation Position: Attention should be paid to the proper installation position to guarantee normal operation and maintenance.
Vertical Installation of Swing Check Valves
While swing check valves are typically installed on horizontal pipelines, they are also suitable for vertical installations when necessary. In such configurations, the medium flows from the bottom to the top of the vertical pipe. However, the choice between horizontal and vertical installation should be made based on comprehensive considerations of pipeline layout and system requirements.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the structural features, installation procedures, and considerations associated with swing check valves is essential for ensuring the efficient operation and longevity of pipeline systems. By adhering to proper installation practices and maintenance protocols, users can enhance system reliability and safety.

