Exploring the Excellence and Challenges of Underground Fully Welded Ball Valves
Underground fully welded ball valves are crucial for fluid control, particularly in addressing seat seal issues from foreign particles or fire incidents. Equipped with a grease injection system, these ball valves offer a swift and efficient solution to potential leaks. By using this type of ball valve, operators can quickly connect a grease gun and use an imported pump to inject sealing grease directly into the seat seal, ensuring a rapid response to critical situations. In the following parts, we will explore the major merits and demerits of the underground fully welded ball valve.
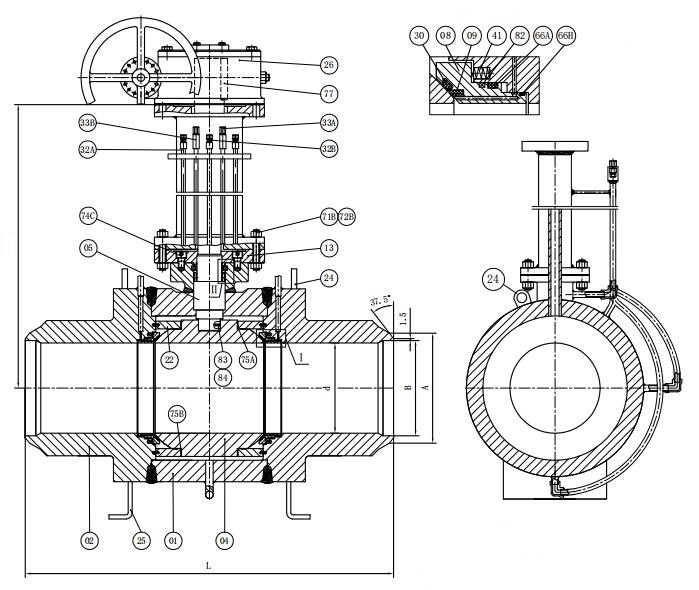
The Major Advantages of Underground Fully Welded Ball Valves
1. Rapid Sealing with Grease Injection
2. Stem Seal Reliability and Low Operating Torque:
3. Full or Reduced Bore Design
4. Extendable Stem
5. Operational Flexibility
Considerations to Keep in Mind about Underground Fully Welded Ball Valves
1. Higher Costs
2. Maintenance Challenges
3. Increased Weight
4. Limited Material Choices
5. Application Specificity
The underground fully welded ball valve stands as an advanced solution, blending enhanced operational features with considerations for robustness and cost implications. As industries progress, understanding the nuanced benefits and trade-offs associated with this valve becomes crucial for informed decision-making in fluid control systems.

The Major Advantages of Underground Fully Welded Ball Valves
1. Rapid Sealing with Grease Injection
- Implementation of a grease injection valve for immediate sealing reinforcement.
- Swift connections to a grease gun and an imported pump facilitate the rapid injection of sealing grease.
- Rapid response to potential leakage problems due to foreign objects or fire incidents.
2. Stem Seal Reliability and Low Operating Torque:
- Dual-sealing approach with a standard sealing gasket and an additional O-ring seal on the filler pressure cover.
- Use of graphite filler and injected sealing grease reduces the risk of stem leakage.
- Stem sliding bearings and thrust bearings contribute to smoother valve operation with lower operating torque.
3. Full or Reduced Bore Design
- The flexibility to choose between full-bore or reduced-bore structures based on specific operational needs.
- Full-bore design ensures alignment of the valve's flow aperture with the pipeline diameter, facilitating easy pipeline cleaning.
4. Extendable Stem
- The valve stem's extendable feature caters to diverse installation or operational requirements.
- Particularly suitable for scenarios requiring the laying of pipelines underground, such as city gas pipelines.
5. Operational Flexibility
- Utilization of seats and stem bearings with a low friction coefficient and excellent self-lubricating properties.
- Significant reduction in the operating torque of the valve, allowing for extended and flexible operation even without sealing lubricating grease.
Considerations to Keep in Mind about Underground Fully Welded Ball Valves
1. Higher Costs
- The complexity and specialization of welding processes may contribute to elevated manufacturing costs.
- Comparatively higher upfront investment when compared to traditional valve structures.
2. Maintenance Challenges
- The fully welded structure poses challenges in terms of maintenance and repairs.
- Replacing seals or performing maintenance tasks may require intricate procedures and specialized skills.
3. Increased Weight
- Robust materials used in fully welded structures contribute to a considerable overall weight.
- Handling and installation may become more challenging, particularly in situations with equipment weight limitations.
4. Limited Material Choices
- Specific materials meeting high-temperature, high-pressure, and corrosion requirements are mandatory.
- Restricted material options may increase procurement costs.
5. Application Specificity
- The unique structure and design of fully welded ball valves may limit their suitability for all application scenarios.
- Certain requirements or conditions may necessitate the use of alternative valve types to meet specific demands.
The underground fully welded ball valve stands as an advanced solution, blending enhanced operational features with considerations for robustness and cost implications. As industries progress, understanding the nuanced benefits and trade-offs associated with this valve becomes crucial for informed decision-making in fluid control systems.

