Comparing Flat and Wedge Gate Valves in Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, gate valves play a crucial role in controlling the flow of fluids within pipelines. Among the various types of valves, flat gate valves and wedge gate valves stand out as commonly used options. These valves exhibit significant differences in their sealing principles, applications, and design characteristics. This article provides an in-depth comparison of these two gate valve types to help readers better understand their pros, cons, and suitable applications.
Flat Gate Valves
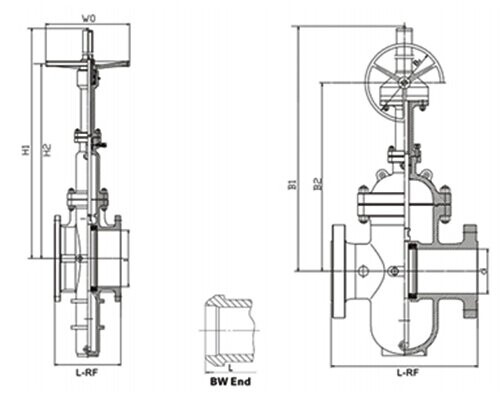
- Strong Bidirectional Sealing: Flat gate valves utilize O-ring seals and pre-tightening force structures, ensuring strong bidirectional sealing performance, making them ideal for applications requiring reliable sealing.
- Unobstructed Passage: With a smooth straight-line passage when fully open, flat gate valves minimize flow resistance and pressure loss, making them suitable for applications requiring unobstructed pipelines.
- Applications: Flat gate valves are well-suited for scenarios involving suspended particle media, bidirectional sealing requirements, and clear passage demands, such as in petroleum and natural gas transmission pipelines.
Wedge Gate Valves
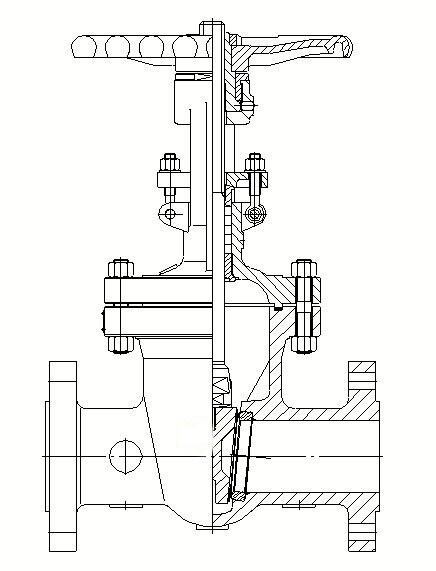
- Single-Side Forced Sealing: Wedge gate valves rely on wedge action to achieve single-side forced sealing, making them suitable for high-pressure environments and applications demanding superior sealing performance.
- Suitability for High-Pressure High-Temperature Environments: Wedge gate valves are suitable for use in high-temperature and high-pressure working media, such as in the electric power industry and petrochemical industry.
- Applications: Wedge gate valves find application in high-pressure, high-temperature environments where stringent sealing and pressure resistance requirements exist, such as in high-pressure shut-off, low-pressure shut-off, and high-temperature media scenarios.
Comparative Analysis
1. Sealing Principle Difference
Flat gate valves employ bidirectional sealing structures, while wedge gate valves utilize wedge action for single-side forced sealing, resulting in distinct sealing principles.
2. Diverse Application Scenarios
Flat gate valves are suitable for bidirectional sealing, unobstructed passage, and suspended particle media scenarios, whereas wedge gate valves excel in high-pressure, high-temperature environments with stringent sealing and pressure resistance demands.
3. Design Characteristic Variation
Flat gate valves feature unobstructed passages, ease of operation, and full closure structures, while wedge gate valves are designed for full open or full close scenarios, with heightened sealing performance requirements.
Flat gate valves employ bidirectional sealing structures, while wedge gate valves utilize wedge action for single-side forced sealing, resulting in distinct sealing principles.
2. Diverse Application Scenarios
Flat gate valves are suitable for bidirectional sealing, unobstructed passage, and suspended particle media scenarios, whereas wedge gate valves excel in high-pressure, high-temperature environments with stringent sealing and pressure resistance demands.
3. Design Characteristic Variation
Flat gate valves feature unobstructed passages, ease of operation, and full closure structures, while wedge gate valves are designed for full open or full close scenarios, with heightened sealing performance requirements.
Flat gate valves and wedge gate valves possess unique design features and are suitable for different application scenarios. Choosing between them requires consideration of specific requirements. Flat gate valves are preferable for scenarios requiring bidirectional sealing and unobstructed passage, while wedge gate valves are better suited for high-pressure, high-temperature environments with stringent sealing and pressure resistance demands.

