Common Check Valve Types and Their Applications
On this page
Check Valves are critical equipment designed to prevent the backflow of media and are widely used in various industrial pipeline systems, such as the outlets of pumps, compressors, and other equipment and devices. By preventing the backflow of media, check valves protect system equipment and avoid damage to the system from backflow. Below is a detailed introduction to several common types of check valves, including their structural features, applicable occasions, and installation requirements.
Vertical lift check valves are primarily used for horizontal pipelines with a nominal diameter of 50mm. They are typically installed at the outlet of pumps to prevent media from flowing back into the system when the pump stops operating. For vertical pipelines, a straight-through lift check valve can be selected to meet the needs.
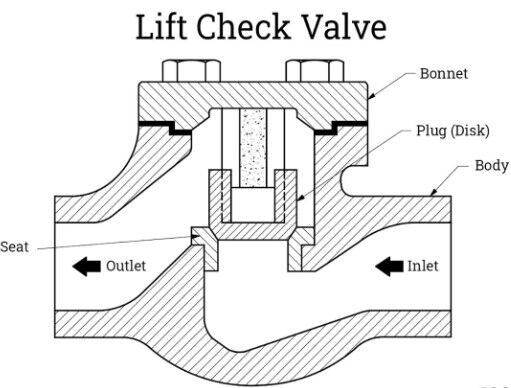
Structure: Features a lift valve design that prevents backflow by the rising and falling of the valve disc, which is usually driven by a spring or gravity.
Advantages: The structure is simple, and maintenance is convenient. It performs well in most standard industrial applications and is suitable for general applications of liquids and gases.
Disadvantages: For high-temperature and high-pressure media, special design or materials may be required to ensure safety and reliability.
Installation Requirements: Usually installed in horizontal pipelines, but for special applications, it can be installed in vertical pipelines. When installing, ensure the valve direction is correct to allow the valve disc to rise and fall smoothly.
Swing check valves are widely used for various media, including water, steam, gas, corrosive media, oils, food, and pharmaceuticals. Their installation position is flexible and can be used in horizontal, vertical, or inclined pipelines.
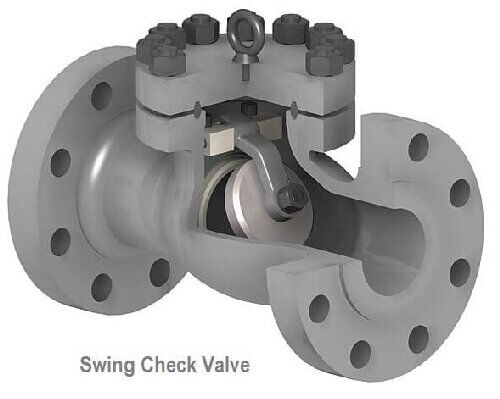
Structure: Closes by rotating the valve disc. The valve disc is generally designed in a circular or semi-circular shape to ensure sealing.
Advantages: Can withstand working pressures up to 42MPa, suitable for high-pressure applications. The maximum nominal diameter can exceed 2000mm, suitable for high flow rate requirements. Capable of adapting to a very wide temperature range, from -196°C to 800°C.
Disadvantages: Requires a larger installation space, and attention should be paid to the opening angle of the valve disc during installation to avoid interference.
Installation Requirements: The installation position is unrestricted, suitable for horizontal, vertical, or inclined pipelines. Ensure the valve direction is correct so that the valve disc can rotate freely and close.
Wafer check valves are suitable for low-pressure, large-diameter applications, especially between two flanges of a pipeline. They are commonly used in applications with large flow rates and low pressure, such as water supply and drainage systems.
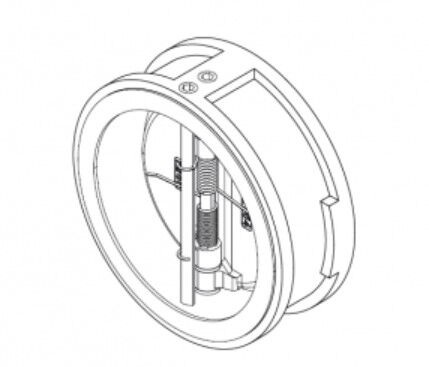
Structure: Features a wafer plate design that prevents backflow by rotating the plate. The wafer plate forms a seal with the valve seat when closed.
Advantages: The nominal diameter can reach over 2000mm, suitable for large flow pipelines. The structure is compact and occupies less space.
Disadvantages: The nominal pressure is generally low, usually below 6.4MPa, and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Installation Requirements: The installation position is flexible and can be used in horizontal, vertical, or inclined pipelines. It is usually installed between two flanges of a pipeline using a wafer connection.
Diaphragm check valves are particularly suitable for pipelines prone to water hammer, especially in municipal water pipelines and low-pressure, ambient temperature applications. They effectively mitigate the water hammer phenomenon caused by media backflow.
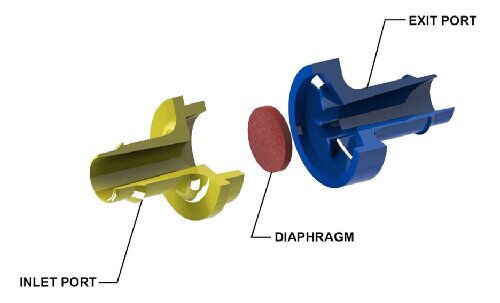
Structure: Features a diaphragm design that prevents backflow by the diaphragm's contact with the valve seat. The diaphragm material is generally an elastic material with good wear resistance.
Advantages: Excellent water hammer resistance, effectively mitigating the impact of water hammer on the system. The structure is simple, and the manufacturing cost is relatively low. The maximum nominal diameter can exceed 2000mm, suitable for large-diameter pipelines.
Disadvantages: The working temperature and pressure are limited by the diaphragm material, usually suitable for low-pressure, ambient temperature pipelines.
Installation Requirements: Best installed in horizontal pipelines, but can also be installed in vertical or inclined pipelines. Ensure good sealing between the diaphragm and the valve seat to ensure effective check function.
Ball check valves are suitable for medium-low pressure pipelines, with the sealing element being a rubber-covered sphere. Due to the design of the sealing sphere, ball check valves have excellent sealing performance and water hammer resistance.
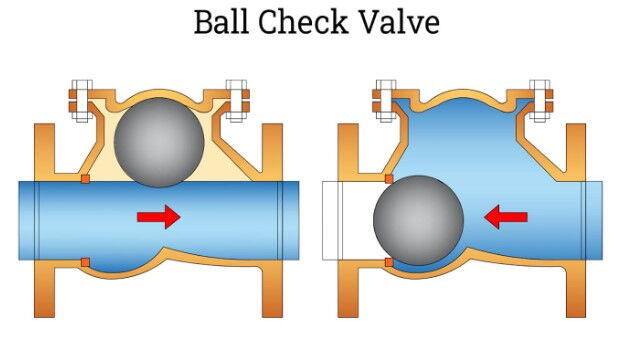
Structure: Features a rubber-covered sphere as the sealing element, which prevents backflow by rotating the sphere.
Advantages: Excellent sealing performance and strong water hammer resistance. The body can be made of stainless steel, and the sealing sphere can be covered with PTFE, suitable for corrosive media. The working temperature range is broad, between -101°C and 150°C.
Disadvantages: Suitable for medium-low pressure environments and not suitable for high-pressure pipelines.
Installation Requirements: Usually installed in horizontal pipelines but can also be used in vertical or inclined pipelines. Ensure good cooperation between the sealing sphere and the valve seat to ensure sealing effectiveness.
Selecting the appropriate type of check valve requires consideration of multiple factors, including the type of media in the pipeline, working pressure, temperature range, and installation location. Different types of check valves have different functions and application scenarios. Understanding the characteristics of each valve can help optimize system design, improve overall operational efficiency, and reliability. In practical applications, the rational selection and installation of check valves can effectively prevent media backflow, protect system equipment, and ensure the safe and stable operation of the pipeline system.
